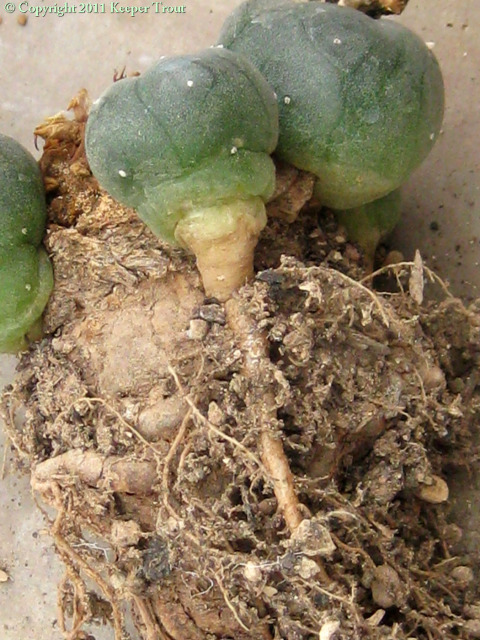
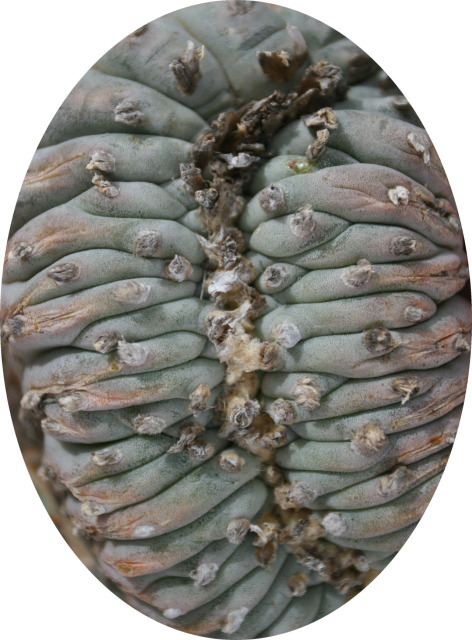
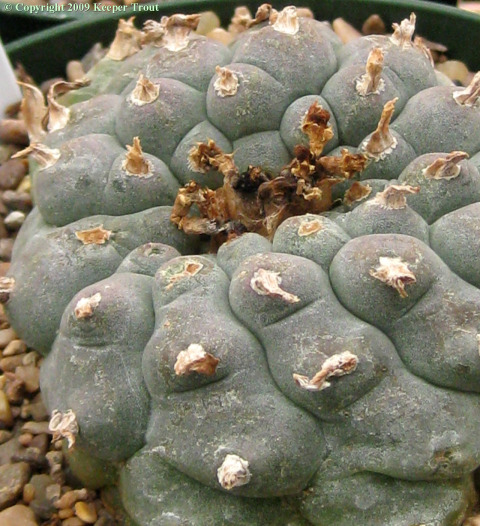
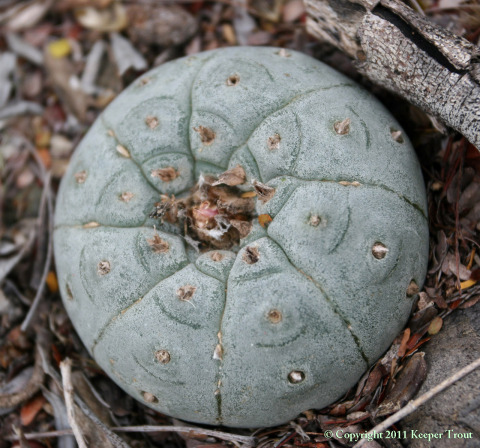
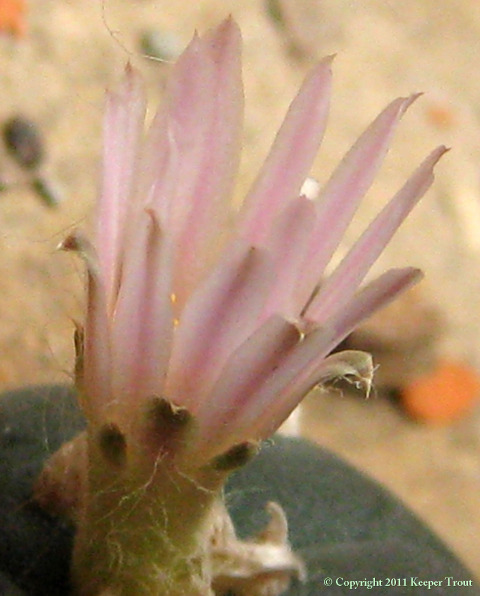
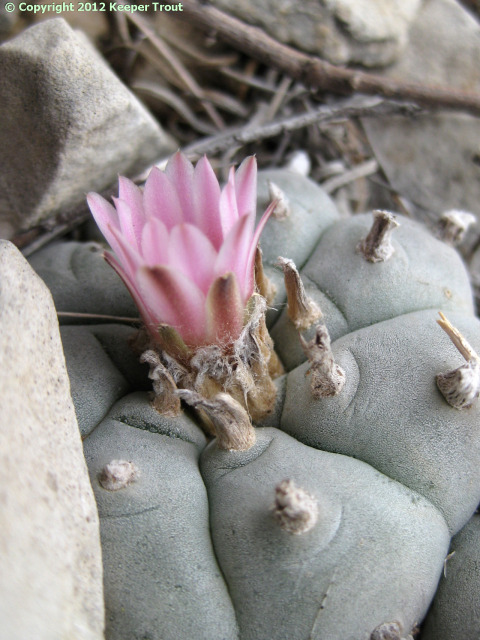
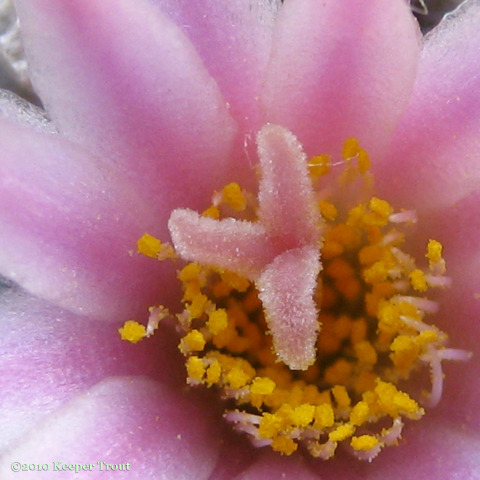
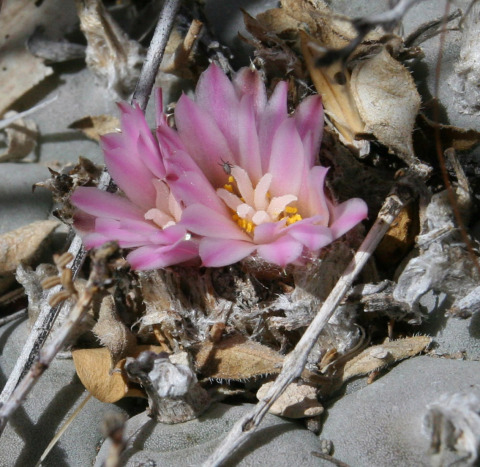
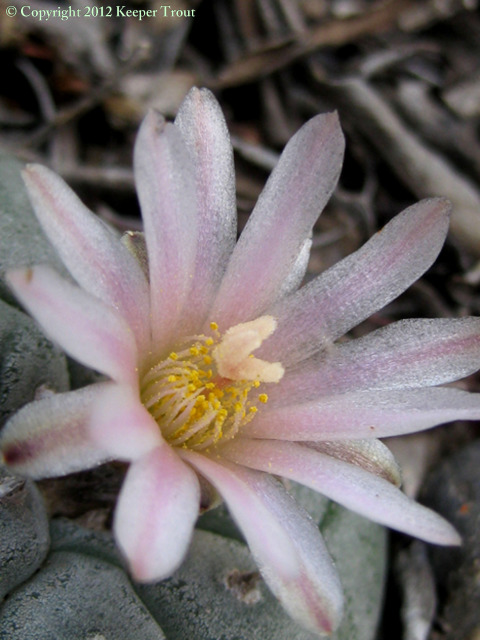
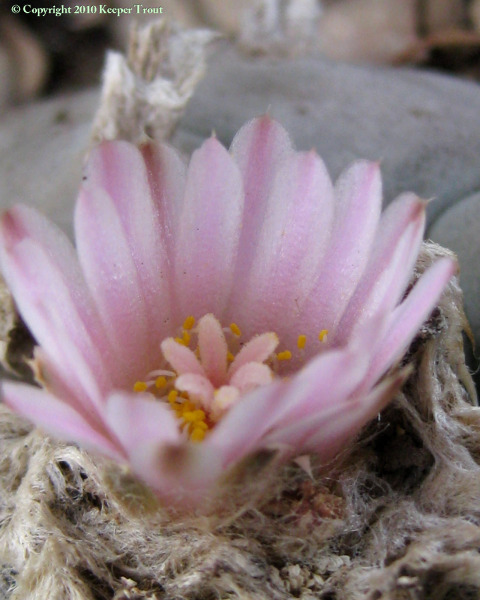
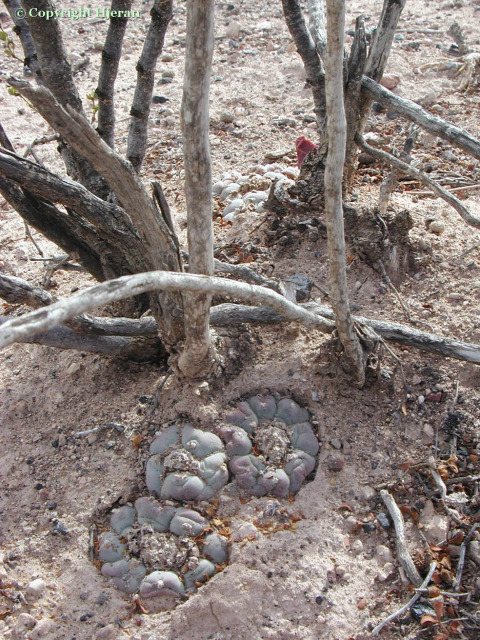
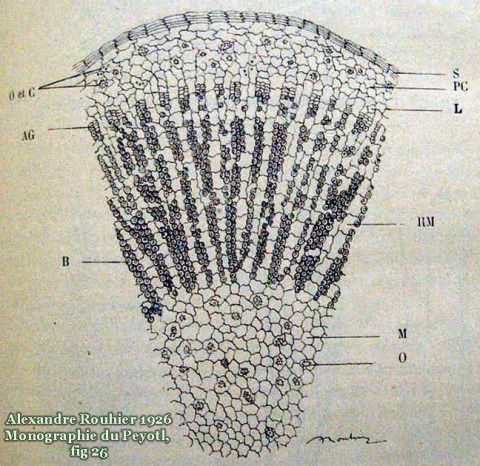
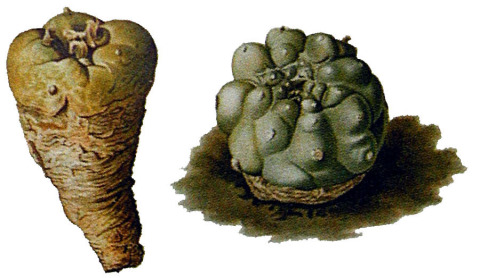
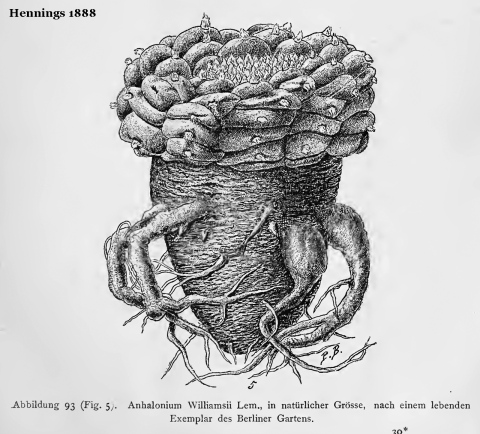
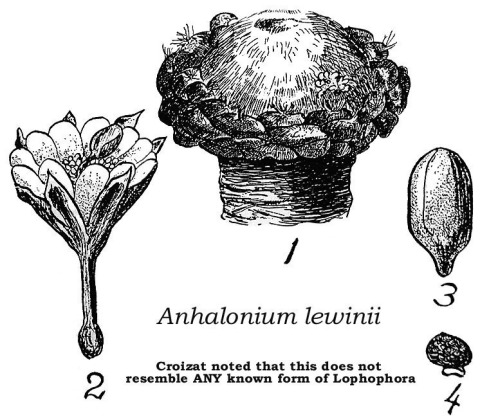
Common names used for peyote or names that have been applied to peyote
azee (’azee’) [14], ’azee’ diyiní [14a], ’azee’ yit’aalii [14b], ’azee’ ch’íidii [14c], bacánoc [37], the bad seed [27] (an erroneous name), bayote [63], bee-sugar [33], beyo [17], biisung [1, 7], biote [37], biznaga [43], cactus [27], cactus buttons [27], cactus-pudding, camaba [37], challote (once a trade name in Starr County, Texas), chaute, chief [27], chiee [37], ciguri [37], devil’s root, diabolic root, the divine cactus, divine herb [37], dope beans [69], dream buttons [46], dry whisky, dumpling cactus, foutouri [8, metaphorical name meaning “flower”], gicuri [21], green whiskey [27], hahaayanx [2], hick-o-kee/hick-oke/hic-o-ke [68], hicoli [21], hicore, hícori [8], hícouri [8], hículi [37], hícuri [8], híkoli [21], híkori [21], híkuli [8, 21], híkuri [8], hikúri [37], hi-kuri [51], hi-kuri waname [51], ho [13], holy chew [62], hos [13], ho-as [11], hoos [36], hoos [36], hoosh [74], houanamé [21], houatari [6], houtari [6], huaname [21], huatari [6], huñka [25], hus [35], icuri [37], Indian cocaine [59], Indian dope [58], jag beans [61], jícoli [21], jícori [8], jículi [37], jicuri [21], jicurite [37], jíkuli, jikuli [55], jíkuri [21], joutori [21], joy beans [56], kamaba [22], kamba [22], kóp [5], likuri [45], L.S.D. cactus [29], makan [1, 15], mascale beans [57], medicine, medicine of God [37], medizin [37], mescal, mescal beans [32], mescal button, mescale, (all names including ‘mesc-’ or variants are erroneous. See 32.), mescalito [27], mezcal buttons [37], moon [27], Mr. William’s Echinocactus [54], muscale buttons [41], muscle buttons [70], natáinoni [1, 9], naw-tai-no-nee [1, 9], nesac’ [24], nezats [24], nicouri [30], nonc-gáiεn [23], o-jay-bee-kee [1, 17], ololiuqui (An erroneous name), opium buttons [75], P [27], pajé [3], pee-yot [9. Now also means “medicine”], peiotl, peodi [47], peote, pejori [16], pejote, pejuta [1, 37a], pellote, peotl [37], peyiotl [44], pie-o-ke [66, 67], peyori [18], peyote bean [60], peyot [64], péyotl, peyotlkaktus [37], peyotlevye (?) [52], péyotl xochimilicensis [42], péyotl zacatecensis [40], peyotyl [49], pezote, pie-o-ke [74], piote, piotl, piule (An erroneous name), piyot [9], plejotl [71], raíz diabólica (By Ortega), Rauschgiftkaktus [37], the sacred mushroom [28] (An erroneous name), schnapskopf [31], sei [10], seni [10], señi [37], sugar [33], teocomitl ahuitzyo [26], teonanacatl [28] (An erroneous name), topi [27], tuna de tierra, turnip cactus, ubadama/ubutama [34], uocoui [37], vegetable whiskey[66], wakoare [65], walena [1, 20], waname [51], wanamo [51], wanamu [51], watara [6], whiskey barrel cactus [38], whiskey cactus, whiskey root[66], white mule, William’s aloëcactus [53], William’s Echinocactus [54], wo-co-wist [4], wohoki [4], wokow [4], wokowi [4], wok-wave/wokwave [75], wokwi [4], the wonderful herb [50], woqui [4], xícori [8], xwucdjuyahi [12], xucladjin-dei [36], xucladjinłndei [39], xos [74].
Also can be encountered in Chinese as cuì guān yù, 烏羽玉 [Wiki] and as 乌羽玉.
These make *great* search terms for imagery.
1. Pre-peyote word meaning “Medicine”, currently used to designate Lophophora williamsii.
2. Arapaho
3. Coahuilteco [More properly, Pakawan; this name was given in Garcia 1760.]
4. Comanche (wokwi and wokowi were said by Mooney to be generic terms for cacti. Stewart similarly gives w gwe i-a as a word for ‘cactus’.)
5. Comecrudo or Carrizo of Tamaulipas
6. Cora of the Tepic Mountains [Rätsch 1998 also gives “chiee” as a Cora name for peyote]
7. Delaware
8. Huichols of Jalisco (and Nayarit)
9. Kickapoo
10. Kiowa (Sei is said by Mooney to be generic for all cacti originating as an older name for prickly pear cacti.)
11. Kiowa Apache
12. Lipan (meaning “pricker one eats”)
13. Mescalero Apaches
14. Navaho (The word ’azee’ means medicine and is used by traditional Navajos to refer to any medicinal substance or material used in a curing ceremony)
14a. Navajo name meaning “Holy medicine”
14b. Navajo name meaning “chewing medicine”; name is used by nonpeyotists
14c. Navajo name meaning “Ghost medicine” ; derogatory name is used by nonpeyotists. Translated as “Devil medicine” in 1940 Tribal Council hearings. [See Note 10]
15. Omaha
16. Opata
17. Otomi
18. Pima of the Gila River region.
19. Shawnee
20. Taos
21. Tarahumare of Chihuahua
22. Tepehuane of Durango [Rätsch 1998 spells “camaba”]
23. Tonkawa of southern Texas
24. Wichita of Oklahoma
25. Winnebago of South Dakota (“The Father Peyote”)
26. Said to have been used by the ancient Aztecs; Schultes 1937b cited Martinez 1928
27. Said to be names used by drug users in the late 1970’s, by Anderson 1980 and/or listed as a street name by Marnell (ed) 1997. The latter also gives “buttons” and “tops” as names for the drug.
28. This is in error but is still occasionally encountered in literature, probably originating with William E. Safford’s mistaken proposal, (among other places in Safford 1916a) that the identity of teonanacatl, the sacred mushrooms, (at that time not yet rediscovered by Western scholars since the persecution of the Catholic Church had driven their use to exist only in secrecy), was in fact dried peyote buttons.
Safford’s reasoning was that, despite peyote and mushrooms being mentioned separately as two obviously different plants, the latter specifically said to be a fungus, they were probably confused by a writer who had never seen the fresh plants [Note 12] The person who was confused was Safford who inexplicably rejected abundant evidence that was available to him.
29. Given as a synonym in Rowley 1978. Gordon Rowley is the only person that I am aware of who has ever used this name.
30. Said by Anonymous 1959 to be used by “the Huichols of Jalisco and the Tarahumares of Chihuahua.”
31. Rauh 1978
32. This name has been, and still is, far more commonly applied to the red seeds of Dermatophyllum secundiflorum (AKA Sophora secundiflora), a small leguminous shrub or tree, than to peyote but it arises from neither one.
Confusion on this point is widely encountered. The etymology of the word “mescal” is clearly associated with the Agave “century plant” as it comes from a Nahuatl word “mexcalli” meaning “cooked agave” so the jump to peyote and then to the red bean is a curious one worth pondering.
All variants of these names (whether given as mescal, muscale or mascal, or similar spelling, and whether it was as buttons or beans) appear to have been saddled onto peyote by Christian reformers as part of a deliberate attempt to present it to the public as a dangerous intoxicant during their intensive activities aimed at achieving prohibition laws against it. See the 2017 presentation by Trout at ESPD50.
Contrary to some popular assertions, the origins of the word mescal have nothing to do with the red bean. Borg 1937 inexplicably claimed it came from a word for fungus but I have not yet found additional support for that. Borg MAY have been confused by W.E. Safford’s confusion.
Two separate theories have arisen as to how the ‘red bean’, as it has usually been called, came to be called the ‘mescal bean’, in one version it was used as an additive to increase the strength of mescal, the other has it arising from a separate etymological origin. Interestingly, peyote was similarly employed as an additive to mescal, it was occassionally mashed with water and ‘fermented’ on its own, and the red beans were added to brewed peyote by a handful of tribes.
Mooney’s assertion that the Mescalero Apaches derived their name from mescal (due to their use of peyote) is pointed out by LaBarre and others to be in error as the Mescaleros were already known by this name well before they became aware of peyote or began to use it.
33. Said by LaBarre to have been the names used by John Wilson (Caddo-Delaware).
34. Japanese name for peyote in Fujita et al. 1972. Ubudama appears to be a misspelling. en.bab.la gives as ペヨーテ.
Wikipedia does as well but also gives Lophophora williamsii as ウバタマ.
Ubutama is also the name of a famous Japanese confectonary that is said to be a bitter red bean paste sweetened with sugar and wrapped in a layer of agar jelly. The name is believed to refer to its shape. It is not clear to me which application of the name came first, the plant or the treat.
35. Given as a name for peyote by Stewart 1987, page 360, in entry 63. Origin is not clear in his note.
36. Given as names used by ‘Apaches’ (Mescalero?). xucladjin-dei is said to be an aboriginal name that has fallen into disuse. Boyer et al. 1968 [in Harner (ed.) 1973]
37. Listed as names by Rätsch 1998: page 327. Rätsch listed many other names that are also in this list. I made note only when his list contained names that were not already included.
37a. Said to be a Dakota word for medicine.
38. Given as the common name by Schneck.
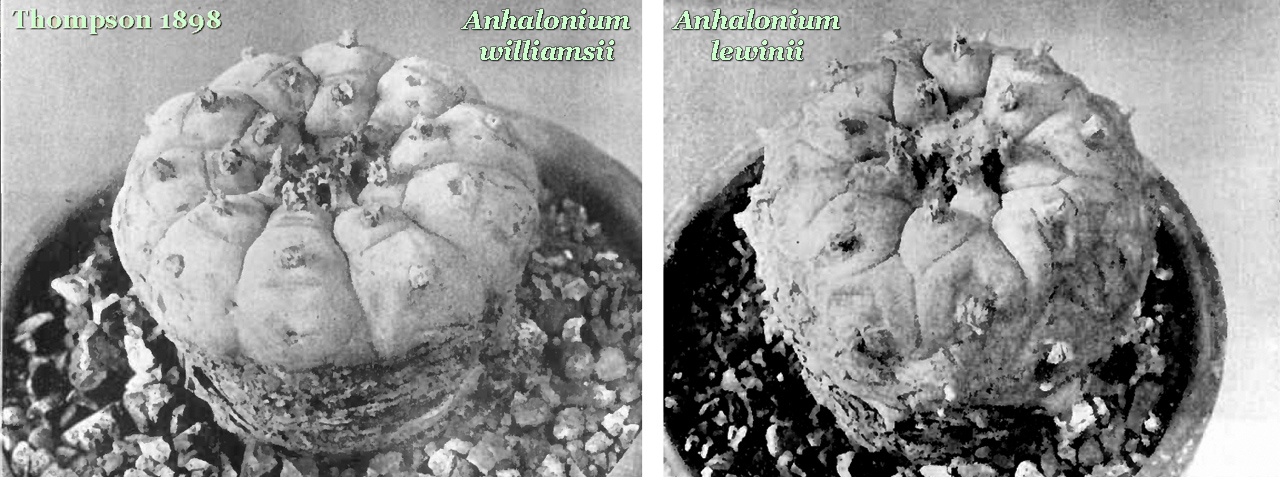
39. xucladjinłndei is given in Castetter & Opler 1936 as the name used by the Mescalero Apache meaning “cactus which they eat”.
40. Name used by Francisco Hernandez and its first binomial.
41. Erroneous name encountered in some of the early literature.
42. Another name used by Hernandez; thought by Anderson 1980 to refer, instead, to Cacavalia cordifolia.
43. Word meaning “carrot”: a generic term used for many cacti.
44. Word used in a French language publication by Benzi 1969.
45. Word given as a Huichol name. Evans 1979.
46. Name used in a 1941 New York Sunday News article
47. Name used in a 1938 Gardenerville Record-Courier (Nevada) article
49. Spelling sometimes appearing in Bulletin on Narcotics articles
50. Name used by Hoebel 1950
51. Names given in Thord-Grey Tarahumara-English Dictionary
52. Russian version of A. Gottlieb’s book has title “Peyotlevye Kaktusy”
53: Name given in Rümpler 1886
54: Name given in Hooker 1847
55: Name given in De Félice 1936
56: Name given in United Press 1909
57: Spelling given in Anon 1908, 1909 & 1911
58: A name used in some pejorative accounts such as Tranter 1942.
59: A name used in 1922 news accounts (examples: Hope Pioneer, 26 October, page 12, Yorkville Enquirer, page 7 and the Washington Evening Star 19 June, page 4).
60: A name used in the 1922 Washington Evening Star, 19 June, page 4.
61: A name used in the 1909 Yakima Herald, 16 June, page 2.
62: A name used in the 1913 The Washington Times, Final Edition, page 7.
63: A name used by Augustine Alba, a Mexican detective, quoted in the 1918 Free Trader-Journal (Ottowa, Illinois), 28 October, page 3.
64: Spanish name given in Jose Arlegui 1737 (1851) Chronica de la provincia de N.S.P.S. Francisco de Zacatecas.
65: Name used by Kiowa; given in Hugh Lennox Scott’s Ft. Sill ledgers.
66: Purported “Indian” name for “whiskey root” given by “The Colonel” in 1857 in The Times Picayune, (New Orleans, LA), 30 September, page 1. This may be the first report in the English language of peyote being referred to as an intoxicant, although the author alludes to the occurrence of an earlier round of correspondence with the editor.
67. Purported “Indian” name for “whiskey root” as given in 1857 The Carolina Spartan, (Spartanburg, SC), 22 October, page 1, and many other papers during 1857 and 1858.
68. Purported “Indian” name for “whiskey root” as given in 1858 Cooper’s Clarksburg Register, (Clarksberg, WV), 7 May, page 1; 1858 Sunbury American, (Sunbury, PA), 24 April, page 4 & 1858 The Abbeville Banner, 4 March, page 4.
69. Name given in 1909 The Salt Lake Tribune, 2 May, page 3.
70. Mis-spelling appearing in Lewin 1888 and persisting into the modern Parke, Davis & Co., company archives.
71. Spelling appearing, in Polish, in Łyko & Piątkowska-Chmiel 2020.
72. Name appearing in Lophophora williamsii entry at Ilife.com.
73. Attributed to Chiricahua in Slotkin 1955. Slotkin expresses some doubt if the Chiricahua were a correct attribution for the word hooshe. This information was derived from JH Jones 1899 A condensed history of the Apache and Comanche Indian Tribes. A contemporary informant names H. Hoijer told him xos meant primarily thorn or cactus but had a secondary meaning of peyote.
74. South Texas circa 1857. Letter to editor of New Orleans Picayune from “The Colonel” in 1857.
75. Said to be called wokewave on the Comanche, Kiowa and Wichita reservation but opium buttons was the name preferred by Clark. Clark 1888.
Common names were collected from many sources, the list above being far from complete. Most are included by Schultes 1937b. Some are simply different spellings (orthographic renderings) of the same name given by people from different linguistic backgrounds. Names with no reference given were encountered in multiple sources and usually had no locale of usage attributed to them (most are English or Spanish).
Peyote is the name that is most frequently used by tribes in the United States and by some in Mexico. Its origin is not clear and various explanations have been proposed. (See Schultes 1937b above, LaBarre 1989 and Anderson 1980 for good discussions. Peiotl is the name used by Fr. Bernadino de Sahagún when describing its use by the Mexican Chichimeca Indians in 1560.
Erronous names were a result of confusion with morning-glory, psilocybin mushrooms or, in the very first example (the “Bad Seed”), possibly Datura.
Atropa belladonna fruit is also called “Moon” (or “Moon pods”) in street vernacular and it is unclear if this drug parlance misnomer is a result of a similar state of confusion or if it is in reference to peyote’s association with moon rites. During the 1970s I encountered ground Datura stramonium seeds being sold ‘on the street’ as dried peyote [Note 11]. Sacramental drugs do not belong in the black-market.
Names equating peyote with alcohol or other drugs are usually derogatory and were generally coined by opponents who were ignorant concerning its actual effects and/or had specific depreciatory intent associated with the promotion of prohibition or drug law activities.
A number of names appear at the Indiana Prevention Resource Center 2008 as purported street names for peyote: Bad seed, Britton, Half moon, Hikori, Hikuli, Hyatari, Nubs, P, Seni, Tops, Topi. I have to wonder just how widely peyote has actually been available as a street drug under some of those names.
Other names encountered in connection with Peyote
Chiculi hualala saeliami: Said by A.V. Frič to be the name used by the Tarahumara for the rare red flowered peyote he encountered in the Sierra Bola, near San Pedro, Coahuila. [Believed to be the same population of plants that were much later named Lophophora fricii]. Frič believed this plant was what had been referred to as “Híkuli walula saelíame” which would be interesting if true since it seems likely to be inactive to sedative if it was actually ever ingested.
Ear-eating: Said by LaBarre to be a term used by some Anadarko Delaware for peyote eating.
Grandfather or Grandfather Peyote: Sometimes used to speak in reverence of the plant. Often used to refer to a large consecrated peyote that is kept in a prominent and sacred place during the peyote ceremony (frequently referred to as the ‘chief peyote ’ or the ‘peyote chief‘.) Normally it is never eaten. So far, only one reference has been encountered to them actually being eaten. This was in an African-American peyote church that once existed. [see Smith 1934.] Stewart 1987 includes Voget’s mention of a Montana Crow stating that he thought the Chief Peyote could be eaten but did not know of any instance when it was.
Hogimá: A Shawnee name for the “peyote chief” (a special button or plant which is used in ceremony, also as a fetish or for power acquisition but rarely if ever eaten.)
Hatzimouika: Huichol tutelary deity for peyote (female).
Híkuli walúla sälíami: Hikuli of great authority. An especially large peyote surrounded by smaller plants, viewed by the Tarahumari as its servants. Special reverence is paid to these plants in deference to their peyote deity (male). [see Lumholtz 1902] Possibly the same as Thord-Grey’s Hi-kuri waru-ra seriame. Said to be the most powerful peyote and to grow buttons up to 12 inches in diameter. Thord-Grey suspected it was a mythical plant.
Hi-kuri owa-me: “Peyote medicine” peyote prepared as drink by Tarahumara shaman [Thord-Grey], owa-me is the Tarahumara word meaning “medicine”
Hi-kuri waname: [Thord-Grey], [Also given as Híkuli wanamé “The Superior Peyote” by later authors] Tarahumara name thought to refer to an especially powerful peyote but it is also thought by others to refer to a Mammillaria or another cacti. [also encountered as Híkuli houanamé; Híkurí-íkuríwa is thought to mean the same.]
Hi-kuri wikara-re: Peyote song (Tarahumara)
Mother Hurimoa: Thought to refer to the Cora peyote goddess.
Seimayi: Kiowa peyote goddess (meaning “Peyote woman”)
Rhaïtoumuanitarihua-hicouri: Huichol differentiation of one of two “kinds” of peyote; this one is thought to have less physiological effects. Meaning “Peyotl of the Goddesses”
Tzinouritehua-hicouri: Huichol differentiation of one of two “kinds” of peyote; this one is thought to be more active and more bitter. Meaning “Peyotl of the Gods”
According to Aberle the following three Navajo terms are used in ceremonies to refer to the peyote:
ni’iln’íí’ sizínii “that which stands in the middle of the earth”
yak’ashbąąh doo bínii ’ohí “nothing is hidden from it from horizon to horizon”
nihook’eh doo bínii’oh “nothing is hidden from it (even) in a storage crypt”
Numerous other plants are also called peyote or by the local native name used for peyote. Some are cacti but many are not. None are known to be hallucinogenic but many are toxic. Not all are active or even used by people for any purpose.
Good discussions or a listing: See Bye 1979, Bruhn 1973, Bruhn & Bruhn 1973, Ott 1993, LaBarre 1989, Ochoterena 1926, Rätsch 1998, Schultes 1937a & 1937b, Slotkin 1955 & Smith 1998/2000.
Many other cacti are equated with peyote or held in similarly high regard. None are known to contain proven hallucinogenic substances unless at exceedingly trace levels. See Bye 1979, Bruhn 1973, Bruhn & Bruhn 1973, LaBarre 1989, Schultes & Hofmann 1980, Smith 1998 & 2000, & Trout Cactus Chemistry By Species 2014 Light for ethnobotanical information on other cactus species thought to be potentially active.
Mescal [Note 13] is a distilled drink prepared from the sap of some Agave species. It arises from the Náhuatl word Mexcalli; for the cooked Agave which is used to make the alcoholic drinks pulque since early times and was distilled into mescal after the Spanish invasion. Mescal buttons as used for peyote arises from early confusion of the effects of peyote with that of alcohol. The word mescal has most often been used in reference to the cooked agave hearts which are eaten as a food.
As Ott 1993 points out, in Europe they certainly had nothing else they could describe it in terms of, and many of the early common names used equated its action with alcohol, such as ‘Dry whisky’, ‘Whisky cactus’, ‘Whiskey root’ or ‘White mule’, a post Civil War name for the plant, which Ott mentions refers to ‘moonshine’ or home-made liquor [Note 14]. Similarly, Rauh’s word: ‘Schnapskopf’ means ‘liquor head’.
Schultes 1937b accurately points out that many native users resent the use of the name mescal, as the associations with alcohol and its attendent evils are totally inaccurate. He also mentions that most of peyote’s opponents have objected to its use due to a misunderstanding or misrepresentation of its effects based on the mistaken presumption that they were similar to alcohol. [Similarly have been presented, by its opponents, the absurd notions that it was variously marijuana, cocaine or opium-like. Sometimes, as was the case with alcohol earlier, this arises from a “tastes-like-chicken” phenomenon when someone is trying to describe something lacking any frame of familiar reference by its comparison with their closest known experience. However, in these cases, this is often chosen with deliberate pejorative or dismissive intent as the intended audience is typically programmed to respond in predictable ways to words like “morphine,” “opium”, “dope” and “hashish”.
It should be suspected that use of the name “LSD cactus” was intended to similarly cast undeservedly perjorative connotations by linking the cactus to the wild oversensationalism and demonification of LSD by the press. Whoever coined the word obviously had no experience with either peyote or LSD.
Mescaline is ‘LSD-like’ only in the same sense that beer is ‘whisky-like’ or opium is ‘heroin-like’; perhaps even less so. While there may be some underlying truth on a generalized and superficial level, this is a deliberate mischaracterization certain to cause a gross misunderstanding of its effects by the uninitiated.